Digital technology moves faster than most business plans. Tools that felt cutting-edge two years ago can now seem outdated, and customer expectations are constantly shifting. In this environment, the question isn’t just how to go digital, but how to stay digital-ready. A future-ready digital strategy is less about adopting every new app and more about creating a foundation for continual change.
Building a future-ready digital strategy based on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) positions the ERP system as the foundational backbone of your organization’s digital transformation. A modern ERP is not just an accounting tool; it is the central platform for data, process integration, and adopting emerging technologies.
Here is a strategic framework, centered on ERP, to achieve a future-ready digital enterprise:
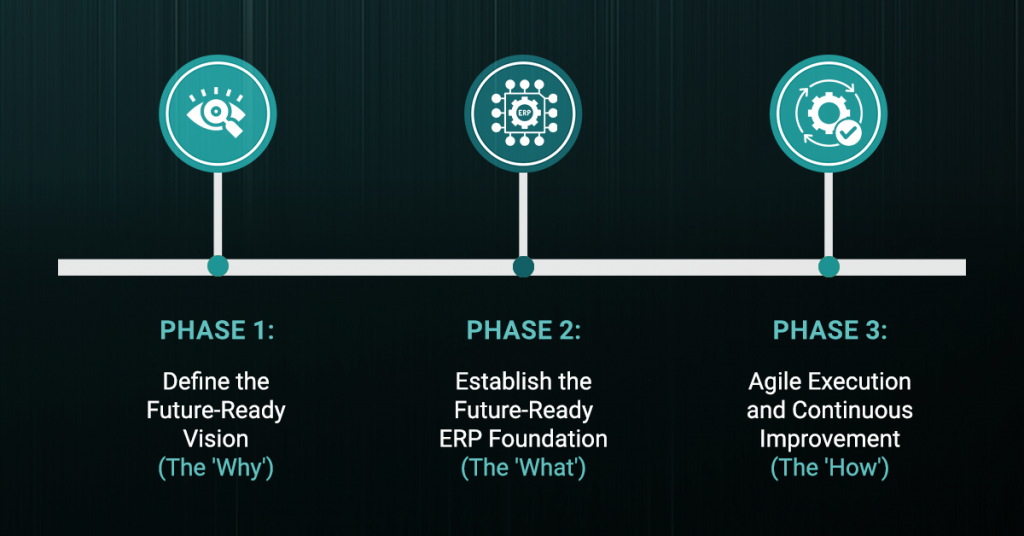
Phase 1: Define the Future-Ready Vision (The ‘Why’)
The first step is to clearly define what “future-ready” means for your business, using the ERP as the primary enabler.
 Align ERP with Business Strategy:
Align ERP with Business Strategy:
Goal: The investment in a new or upgraded ERP must be driven by business objectives like increased market competitiveness, better customer service, and improved financial results, not just replacing an old system.
Action: Define a clear digital vision for the company that is directly enabled by the new ERP’s capabilities, such as greater agility and operational efficiency.
 Evaluate Current State and Identify Gaps (Diagnostic):
Evaluate Current State and Identify Gaps (Diagnostic):
Goal: Understand your starting point.
Action: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of your existing IT environment and business processes. Identify inefficiencies, data silos, and integration gaps that a modern ERP needs to solve.
 Define Success Metrics and Investment (KPIs & ROI):
Define Success Metrics and Investment (KPIs & ROI):
Goal: Establish a framework for measuring transformation progress and justifying the financial commitment.
Action: Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that directly tie back to your strategic objectives (e.g., faster financial close, reduced operational costs, improved on-time delivery metrics). Crucially, model the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and create a detailed return on investment (ROI) plan to justify the massive investment and internal resource allocation.
Phase 2: Establish the Future-Ready ERP Foundation (The ‘What’)
The core of the strategy lies in transforming your ERP into a scalable, intelligent, and agile digital platform.
 Centralized Data and Governance (The Single Source of Truth):
Centralized Data and Governance (The Single Source of Truth):
Goal: Break down silos and ensure data consistency across the enterprise, acknowledging the multi-system reality.
Action: Establish an Enterprise Information Model (EIM) to create common data definitions. Centralize transactional data within the ERP. Recognizing that modern organizations use a multi-system ecosystem (CRM, SCM, etc.), establish a Data Integration Layer or Data Warehouse (DWH) to aggregate and normalize data from all sources for enterprise-wide reporting and advanced analytics.
 Process Re-engineering and Standardization:
Process Re-engineering and Standardization:
Goal: Optimize end-to-end business processes before automating them.
Action: Use the ERP implementation as an opportunity to redefine and streamline operational processes to align with industry best practices embedded in the ERP. Standardize workflows across functional units to maximize efficiency. Simply applying new technology to old, inefficient processes is not effective.
 Invest in Emerging and Scalable Technologies (Cloud and Composable):
Invest in Emerging and Scalable Technologies (Cloud and Composable):
Goal: Ensure the platform can adapt to future innovations.
Action: Choose a Cloud or Hybrid-Cloud ERP solution for greater scalability, flexibility, and an “evergreen” operational model that receives continuous updates. Look for features like low-code/no-code platforms and a composable design. Critically, evaluate the vendor’s innovation roadmap, API strategy, and partner ecosystem to ensure the platform will remain “future-proof” for the next decade.
 Secure the Digital Backbone (Governance and Compliance):
Secure the Digital Backbone (Governance and Compliance):
Goal: Protect centralized core data and ensure continuous regulatory adherence.
Action: Embed robust Data Governance and Security controls from day one. Implement role-based access and necessary security measures, highlighting the need to maintain global regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) given the concentration of sensitive data in the cloud environment.
 Integrate Intelligent Capabilities (AI-Ready Data):
Integrate Intelligent Capabilities (AI-Ready Data):
Goal: Transform data into actionable insights and automate workflows.
Action: Prepare your data to be “AI-ready.” Adopt an ERP that leverages AI and Machine Learning for capabilities like predictive analytics (forecasting and anticipating supply chain disruptions) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for automating manual tasks (e.g., data entry, invoice processing).
Phase 3: Agile Execution and Continuous Improvement (The ‘How’)
To maintain a “future-ready” state, the implementation and operation of the ERP must be agile and iterative.
 Adopt an Agile/Hybrid ERP Implementation Methodology:
Adopt an Agile/Hybrid ERP Implementation Methodology:
Goal: Reduce risk, accelerate time-to-value, and ensure user alignment.
Action: Move away from a rigid Waterfall approach. Utilize a phased or iterative deployment (Agile/Scrum), breaking the project into small, manageable sprints. This allows for early, frequent testing, gathering user feedback, and adapting to changing requirements without significant delays.
 Focus on Change Management and Workforce Upskilling:
Focus on Change Management and Workforce Upskilling:
Goal: Drive high user adoption and build digital readiness.
Action: Implement a robust Change Management strategy. Involve end-users, IT, and leadership early on. Provide role-based training and support to help the workforce adjust to new processes. A skilled team is essential for leveraging the full value of the ERP system.
 Embed Customer-Centricity:
Embed Customer-Centricity:
Goal: Use the ERP’s unified data to enhance customer experience.
Action: Leverage the ERP’s ability to centralize customer data (often integrated with CRM) to provide a 360-degree view of the customer. This enables personalized experiences, faster response times, and an improved end-to-end service journey.
 Establish a Continuous Improvement Model:
Establish a Continuous Improvement Model:
Goal: Ensure the ERP system and processes evolve with the business.
Action: Regularly monitor the defined KPIs and use real-time data from the ERP to assess performance. Establish a feedback loop for continuous iteration and improvement, ensuring the system remains aligned with new technologies and shifting market requirements.
Culture makes or breaks a digital strategy. Future-ready organisations encourage experimentation, rapid learning and cross-functional collaboration. They scan the horizon for emerging technologies but adopt them selectively, running small pilots before scaling up. This mix of curiosity and discipline keeps them nimble even as the landscape changes.
Becoming future-ready is not about predicting every technological shift, it is about building the agility to respond to them. A modern ERP-led digital strategy creates that foundation. By aligning business goals with technology, unifying data and processes, and embedding intelligence and adaptability into operations, organizations can stay resilient in the face of change. The most successful enterprises will be those that treat digital transformation not as a one-time initiative but as a continuous journey where the ERP evolves alongside the business to power innovation, efficiency, and growth.