There is no doubt that we live in an increasingly unpredictable environment. Yet finding an opportunity in every adversity is what we should aim for!
The global economic and technological system is changing at a faster rate than ever before. Prior to the pandemic ‘digital’ was a watchword among businesses around the world, with most companies researching new digital technologies for transition. However, as the pandemic continued to distress the world, many organizations’ pushed through their digital transformation plans in 2021. This trend of digital adoption is expected to continue in 2022 too.
So, what exactly does “digital transformation” mean? Is it merely a trendy way of saying “transitioning to the cloud”? What aspects of our company’s strategy should be revised when going digital? Is it truly worth the effort?
The term “digital transformation” can be interpreted in a variety of ways. Some describe it as the methods of adopting SaaS applications or cloud infrastructure techniques. However, when we define it fundamentally, it is more about focusing on redesigning a company’s processes using digital techniques to generate value and achieving corporate success.
The significance of ERP in digital transformation
According to a Gartner report, the ERP market which expanded at a rate of 8.8% in 2019 and valued at $38.8 billion, is expected to grow at the rate of 7% annual pace in constant currency and with a market value of $44 billion through 2022. However, according to experts, these figures may actually cross the predictions, as the pandemic has resulted in a surge in ERP sales globally as businesses started focusing on establishing flexible supply chains, which has become a crucial aspect for enterprises from the onset of crisis.
An ERP software provides a consolidated picture of different business functions. Simply said, an ERP refers to an umbrella system that helps in managing inventory, accounts, transactions, resources, and production. Furthermore, it provides a unified platform for managing different vendors and customers. Advanced ERP systems have incorporate emerging technologies like Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine learning. Such ERP systems can provide businesses with an overall view of their operations along with an ability to act on them seamlessly, allowing you to quickly resolve any gaps.
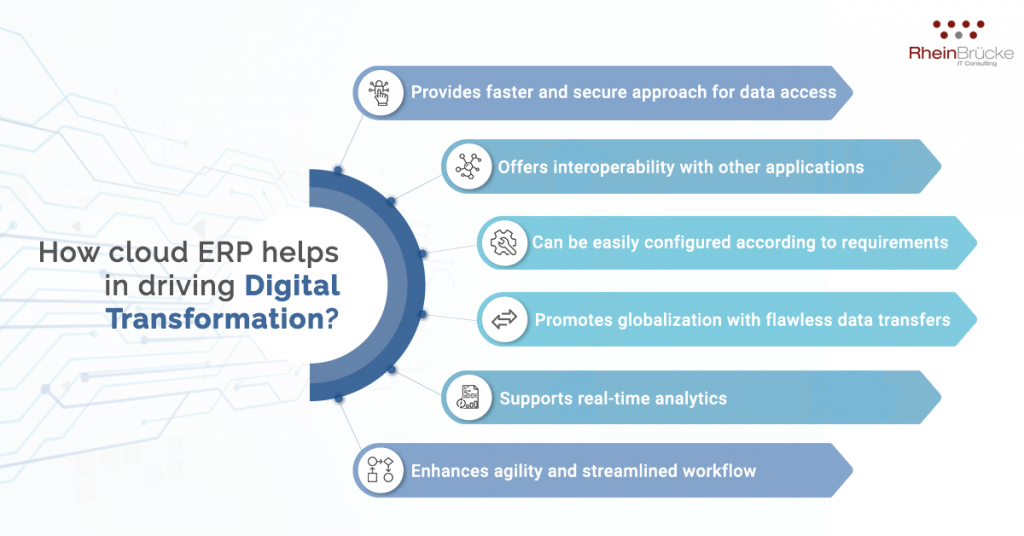
What Role Does Cloud ERP Play in Driving Digital Transformation?

The two most prevalent forms of ERP systems are on-premise and cloud. The key difference between on-premises and cloud-based ERP is in the way the software is deployed and accessed. On-premise ERP systems are deployed locally on the organization’s PCs and servers, whereas a Cloud ERP, also known as SaaS or Software-as-a-Service, is hosted on the internet “Cloud” and delivered as a subscription service by the vendor.
Cloud ERP plays a significant role in digital transformation and has also grown in popularity over the last few years. A report by Panorama Consulting revealed that a large percentage (62.70%) of organizations have opted for cloud ERP software over on-premise software. Due to its flexibility and compatibility with latest technologies such as Industry 4.0, Cloud ERPs are helping organizations to innovate while also providing a competitive advantage.
What ERP trends are expected to persist in 2022?
ERP driven digital transformation proceeded at a rapid rate in 2020 and 2021 due to the pandemic and it is expected to show an upward trend in the coming year as well. ERP market statistics also reveal that the market for new technologies and tools is expanding, and organizations are ready to adopt and work with innovative techniques.
Here’s a list of the top ERP trends that will continue to emerge in 2022:
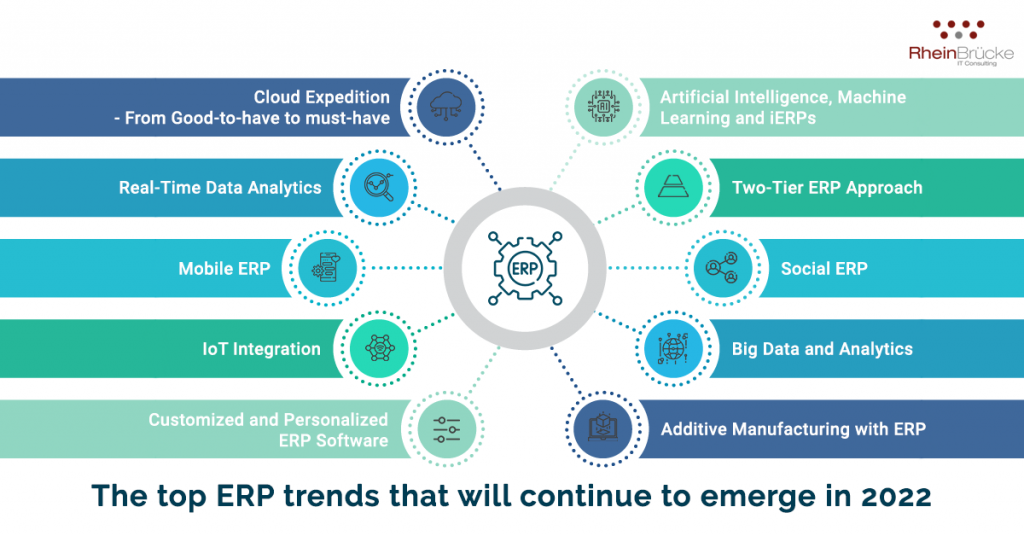
1. Cloud Expedition – From Good-to-have to must-have

Although Cloud-based ERP isn’t the newest trend, but it is still the most revolutionary one. With the rise in cloud-hosted choices, companies are gaining an advantage in terms of effective work methodologies, timelines, minimum total cost of ownership and affordability to small and medium-sized businesses.
A rising number of firms are also adopting hybrid ERP systems, which is a combination of on-premise and cloud-based ERP systems. According to a study, 51% of CIOs use cloud ERPs, 35% prefer on-premise systems and 10% chose hybrid ERP software to get the best of both worlds. Number of companies migrating to Cloud ERP is expected to rise in the future.
2. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and iERPs

In the coming year, the rising AI trend will reverberate throughout all ERP features. A survey report by UST SMartOps reveals that 15% of CEOs believe that artificial intelligence (AI) has the capability of affecting an ERP software fundamentally. Thus, it can be said that AI is leading the change to automate nearly every corporate management activity. Its features such as face recognition, enable users to have a more secure and customized experience.
Machine learning is another aspect that has transformed the way ERP software operates, particularly in the manufacturing industry. When integrated with an ERP, data may be fed to AI algorithms allowing companies to uncover patterns in workflows. iERP solutions (an acronym for ERP with intelligence technology integration) are intelligent ERPs that can automate processes, eliminate mistakes, and shorten the time it takes to input data.
3. IoT Integration

IoT integration is critical for digital transformation in terms of automation. It enables ERP systems to process enormous volumes of data in real-time without any need of establishing interfaces with external sources of device data aggregation. It is anticipated that 35 billion IoT devices would be deployed by the end of this year, with more than 75 billion installed by 2025, leading the global IoT spending to exceed an estimation of $1.4 trillion.
4. Mobile ERP

Mobile ERP software, like Cloud ERP, gained prominence at the time of global lockdown, when organisations began to investigate fresh methods to exploit mobile capabilities as an extension to the ERP systems. Mobile ERP applications are intended to support operations “on the go”, including apps like warehousing, sales and services, POS (Point of sale), employee attendance records and many more.
5. Big Data and Analytics

Today, companies are increasingly seeking analytics-based solutions as they value the capacity to make data-driven choices rapidly. According to a poll, firms that make use of advanced analytics can perform two times better financially, take five times faster time-sensitive decisions and can execute plans and decisions three times more effectively.
According to current trends, both business and government organisations are redesigning their operations to operate with big data analytics software. In fact, businesses that use big data have seen profit increases of 8 to 10%.
6. Customized and Personalized ERP Software

ERP solutions in the future will have a more robust user interface. They will also become more customer-specific, adaptable, and accessible. Furthermore, the tools would be simple to use not just for developers or IT personals, but for everyone. Also increased levels of customization are expected in the future ERP systems that could also support cutting edge technologies like AI, analytics and IoT.
7. Social ERP
Like social networking platforms, social ERP applications encourage cooperation and communication across departments and workers. Such systems are highly beneficial, especially for manufacturing, distribution or retail sectors, where following up with the clients, identifying patterns and alerts regarding purchases and returns is critical.
8. Two-Tier approach
To meet the demands of big enterprises with many locations and/or subsidiaries, the two-tier ERP strategy effectively employs “two systems.” In this approach, the organization uses a tier 1 ERP system to manage the day-to-day activities of the headquarters which requires more sophisticated functionalities to run global operations, whereas the subsidiaries use a tier 2 ERP which is less resource-intensive and capable to meet requirements such as location-specific operations and compliance.
9. Real-Time Data Analytics
ERP systems are increasingly focusing on providing organisations with a way to acquire trustworthy information in real-time. Real-time data can help organizations in streamlining business operations, enhancing customer experience and efficiently monitoring data by integrating with new technologies.
10. Additive Manufacturing with ERP

Adoption of additive manufacturing, often known as 3D printing, has paved the path for new manufacturing ERP trends. Larger, more complicated 3D printers enable firms to reduce costs and improve process efficiency. An ERP system can assist in tracking the amount of material required for 3D printing production. Besides this, it can track each product throughout the full production process. This technique of system auditing will become more prevalent in the following years as many manufacturing industries are actively deploying 3D printers. According to the Sculpteo survey, 51% of businesses use 3D printers in their manufacturing process. This number will only rise in the future if current trends continue.
Conclusion

We’ve already passed the phase where ERP was solely available to large businesses. Because of the advent of cloud computing, modular systems, and other technical breakthroughs, smaller firms may now benefit from them as well. According to a report by IDC, global digital transformation spending is expected to exceed $1.97 trillion by 2022.
More developing trends will undoubtedly emerge in 2022 and beyond, since development never stops, but rather accelerates. So, let’s all look at the best path forward on our digital transformation journey for ERPs.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you require any support with your ERP.